

The Systems Management Console allows you to monitor events across a multimachine architecture or in a standalone environment, and to view the status of individual services and agents. With the appropriate permissions, you can also use the Systems Management Console to perform administrative tasks, such as starting or stopping a service.
To start, stop, or restart services, the Systems Management Console interacts with the JMX agent running in each installation. The agent is itself a lightweight server that accepts network requests from the Systems Management Console.
![]() Since Systems Management is an EAServer application,
you cannot use the Systems Management Console to start or restart
the server that is hosting the Systems Management application.
Since Systems Management is an EAServer application,
you cannot use the Systems Management Console to start or restart
the server that is hosting the Systems Management application.
![]() Connecting to the Systems
Management Console
Connecting to the Systems
Management Console
In your Web browser, go to:
http://host:8080/WebConsole
Where host is the name of the server that hosts the Systems Management application. The default host is the machine name.
In the login window, enter:
User Name – a valid EAServer user name.
Password – the password for the user name.
Once you are logged in, you see a multi-pane window that consists of:
Banner – contains links that allow the user to log out, and to obtain online help.
Footer – displays the user who is currently logged in.
Details view (right pane) – displays detailed information about a selected item in the tree view, and allows you to perform operations on services.
Tree view (left pane) – contains a hierarchical overview of the various components that are accessible through the console. There is a node under JMX Browser for each host server that the console knows about. Under each of these nodes are the following folders:
Services The Services folder contains all the services that have been installed. A service is simply an MBean with a well-defined lifecycle that has been registered with the ServicesManager MBean. All services have the same interface presented through the Systems Management Console. For each service, you can view basic information about it, and perform a number of operations on it, such as starting it, or viewing its log file.
Events The Events folder allows you to view events that have been recorded on the JMX agent. These are events that correspond to JMX notifications, raised by certain system components.
MBeans The MBeans folder provides access to the underlying MBeans, including those MBeans that are displayed as services. For information about the MBeans whose attributes you can configure and whose operations you can perform, see “Accessing MBeans”.
You can highlight a node in the tree view, and see details associated with it in the property view.
When you are logged in to the Systems Management Console, the MBeans and services that are visible are determined by the J2EE roles that you have been granted. A service can be associated with certain read and update roles. This means that users must be granted these roles before they can view, or perform operations on, the service. For example, the EAServer service might have a read role called ReadX, as well as the default Admin Role. To view the EAServer service, users must be granted either the ReadX role or the Admin Role. By default, a service can be operated on only by someone who has the Admin Role—see “Managing user roles”.
When you first log in, the tree view is collapsed. Use the plus sign to expand the tree view; your Web browser displays two panes similar to those shown in Figure 13-1. The tree view in the left pane expands and collapses to show the hierarchical view of managed services. When you highlight a specific item in the tree, detailed information about the item displays in the details view in the right pane. In the tree view, you can expand items by clicking on the plus-sign icons next to each folder, and collapse the hierarchy by clicking on the minus-sign icons. Items that do not display a plus-sign icon cannot be expanded.
Figure 13-1: Systems Management Console
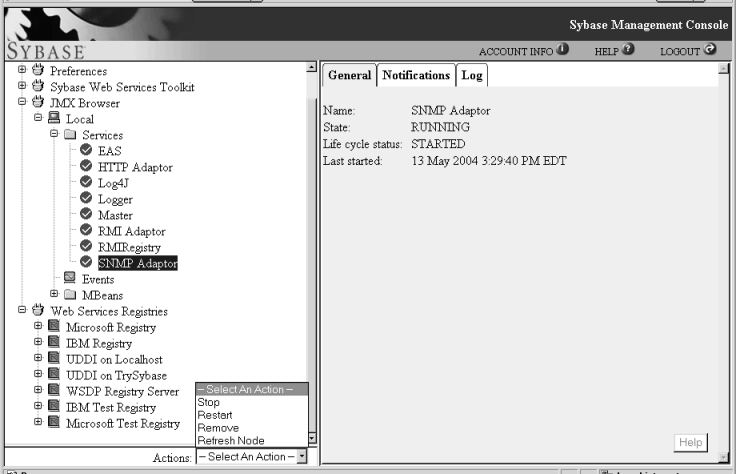
The details view displays information about the item you highlight in the tree view.
When you select JMX Browser in the tree view, the details view displays a list of the installed servers.
When you select a server in the tree view, the details view displays the following information:
Profile Name – the name of the server profile, such as “Local.”
Host Name – the name of the machine hosting the server.
Port – the port where the server listens for connections; the default is 1099.
Principal – user name for the JMX agent on the remote machine.
Credentials – password for the JMX agent on the remote machine.
Trust Store – name of the trust store.
Key Store – name of the key store file.
Password – password for the key store and trust store.
Connect at login – check box; by default, unchecked.
When you select a service in the tree view, the details view displays these tabs:
General Information about the service.
Name – the name of the service, such as “SNMP Adaptor.”
State – the state of the service, which can be:
STARTING
RUNNING
STOPPING
STOPPED
FAILED
Life Cycle Status – the current state of the service’s lifecycle, which can be:
NOTINSTALLED
INSTALLED
INITIALISED
STARTED
STOPPED
TERMINATED
FAILED
Last Started – the time the service was started.
Notifications This section displays notifications generated in connection with the service; for example, if the SNMP master agent goes down. If this happens, State displays as “FAILED” but the Life Cycle Status displays as “STARTED,” which means that the service started but has since gone down. Life Cycle Status indicates what has been done to the service; for example, started or stopped. State displays the current state of the service. If a service fails, a warning triangle also displays next to the service name in the tree view.
Log Displays the log. To display only part of the log, enter the number of lines you want to see.
When you select Events in the tree view, the details view displays a list of the most recent events. To display a subset of the events, enter the number of lines you want to see.
When you select MBeans in the tree view, the details view displays a list of the installed MBeans. When you select a specific MBean in the tree view, the details view displays the MBean attributes, which vary according to the MBean. “Accessing MBeans” describes the MBeans you can configure and the operations you can perform.
To perform an action on one of the entities in the tree view, highlight the entity, click Actions at the bottom of the page, and select the appropriate action from the list. Table 13-7 defines the actions for each entity type.
User roles are determined by the EAServer security system, including Enterprise Security, if it is installed. Roles are not part of the Systems Management framework.
By default, users who have been granted the Admin Role can view all the services and MBeans that are deployed in the JMX agent, and can perform operations, such as starting and stopping services. You can also configure your system to allow users with roles other than the Admin Role to perform these tasks.
Tighter controls exist for the roles required to access or operate on a service when it is accessed via the Services folder in the Systems Management Console. To configure these roles, you must edit the XML file that is used to start and configure the service. Every service can be assigned a set of read roles, and another set of update (execute) roles. If a service has no associated roles, it defaults to the values defined on the servlet’s Init-Params tab.
To assign a set of roles to a service, edit the appropriate XML file, and change the service definition. The XML files are located in the Systems Management ROOT directory; the EAServer service XML file is eas.xml.
Assume that you want to require that to view the EAServer service, users must have been granted either the ReadRole or Admin Role, and to do anything to the service (execute a method, or change an attribute) users need either the UpdateRole or Admin Role. To configure this scenario, the contents of eas.xml should look something like this:
<service name="EAS" type="product" mbean="sybase.system.service:Type=EAS,Name=Jaguar" startmode="automatic" readroles="ReadRole, Admin Role" updateroles="UpdateRole, Admin Role" </service>
Instead of specifying “Admin Role,” you can use “+” to indicate the default role or roles specified on the servlet’s Init-Params tab.
In this example, to see and update the EAServer service, you must be granted either Admin Role, or both ReadRole and UpdateRole. If you are granted only ReadRole, you can view the EAServer service details but not update it. If you are granted only UpdateRole, you cannot see the service, so you cannot update it either.
For more information about user roles, see the EAServer Security Administration and Programming Guide. If Enterprise Security is installed, see also the Enterprise Security Administration Guide.
Using the Web Console, you can access the following MBeans to manage your system:
The attributes you can modify and the operations you can perform for each of these MBeans is described below.
| Copyright © 2005. Sybase Inc. All rights reserved. |

|
|